Understanding the Different Types of Dental Handpieces
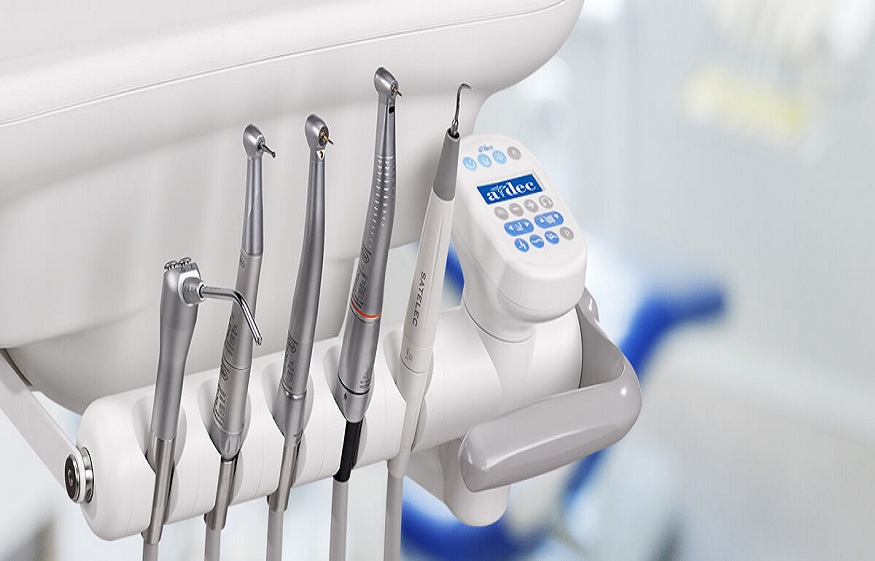
Dental handpieces are essential tools in modern dentistry, enabling precision, efficiency, and patient comfort during a wide range of procedures. From routine cleanings and cavity preparations to more complex restorative or surgical treatments, handpieces are a dentist’s most versatile instruments.
Choosing the correct handpiece for a specific procedure is vital for ensuring optimal results and patient safety. Different types of dental handpieces offer varying speeds, torque, and functionality, making it important for dental professionals — and even patients curious about the tools used — to understand their differences.
In this guide, we’ll explore the different types of dental handpieces, their uses, and the benefits they provide in modern dental practice. Whether you’re a dental professional, a student, or a patient wanting to better understand your treatment, this article provides a comprehensive overview of these essential tools.
1. High-Speed Dental Handpieces
High-speed handpieces are among the most commonly used in dental practices:
- Speed and Efficiency: Operate at speeds up to 400,000 rotations per minute (RPM), allowing dentists to remove decay or shape teeth quickly.
- Cooling Systems: Typically equipped with water spray to prevent heat damage to teeth.
- Precision: Ideal for cutting enamel, removing old restorations, and preparing teeth for fillings or crowns.
High-speed handpieces are essential for procedures that require precision and speed, making treatments faster and more comfortable for patients.
2. Low-Speed Dental Handpieces
Low-speed handpieces operate at significantly lower RPMs, offering more control and torque:
- Versatility: Used for polishing teeth, removing soft decay, finishing restorations, and adjusting prosthetics.
- Comfort: The slower speed reduces vibration and noise, enhancing patient comfort.
- Attachments: Can accommodate a variety of burs, brushes, or polishing tools for different procedures.
Low-speed handpieces are particularly useful for tasks that require fine control rather than rapid cutting.
3. Electric Dental Handpieces
Electric handpieces are becoming increasingly popular due to their consistent performance:
- Constant Torque: Maintain speed even under pressure, allowing for smoother cutting.
- Reduced Noise: Often quieter than traditional air-driven handpieces.
- Precision: Improved control for delicate procedures like endodontics or crown preparations.
Electric handpieces can improve efficiency, reduce fatigue for the dentist, and increase patient comfort during treatment.
4. Air-Driven (Pneumatic) Handpieces
Air-driven handpieces use compressed air to rotate the bur and remain a staple in many dental practices:
- Lightweight: Easier to handle for prolonged procedures.
- High-Speed Capability: Ideal for quick cutting and preparation tasks.
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than electric alternatives.
While highly efficient, air-driven handpieces may lose speed under pressure, which is something dental professionals need to consider for precision procedures.
5. Surgical Handpieces
Surgical handpieces are specialised tools used in oral surgery and implant procedures:
- High Torque: Can cut through bone efficiently without stalling.
- Sterilisable: Designed for repeated sterilisation without compromising performance.
- Compatibility: Often used with specific burs for implant site preparation or tooth extractions.
These handpieces are crucial for procedures requiring both power and precision, ensuring safety and accuracy in surgical contexts.
6. Prophylaxis (Polishing) Handpieces
Prophylaxis handpieces are specifically designed for cleaning and polishing teeth:
- Low-Speed Operation: Gentle enough for routine hygiene treatments.
- Rotary Cups or Brushes: Attachments allow effective removal of plaque and stains.
- Patient Comfort: Minimal vibration and noise make the experience more pleasant.
These handpieces are essential for maintaining oral health and enhancing the cosmetic appearance of teeth.
7. Contra-Angle Handpieces
Contra-angle handpieces are characterised by their angled head, allowing access to hard-to-reach areas:
- Versatile: Can be used for restorative, prophylactic, and surgical procedures.
- Precision: Provides better visibility and control in posterior areas of the mouth.
- Attachment Flexibility: Compatible with a wide range of burs and polishing tools.
The angled design makes these handpieces invaluable for precise work, especially in tight spaces.
8. Fibre-Optic Dental Handpieces
Fibre-optic handpieces incorporate built-in lighting to improve visibility:
- Illumination: Direct light at the cutting area enhances accuracy and reduces eye strain.
- Integration: Often used with high-speed or low-speed models for enhanced performance.
- Patient Safety: Improved visibility helps prevent accidental damage to soft tissue or adjacent teeth.
Fibre-optic technology is a valuable advancement in modern dentistry, improving both efficiency and safety.
9. Air-Turbine vs Electric: Key Differences
Understanding the difference between air-turbine and electric handpieces is important for dental professionals:
- Air-Turbine Handpieces: Lightweight, high-speed, and cost-effective but may lose speed under load.
- Electric Handpieces: Provide consistent torque, greater control, and quieter operation but are typically heavier and more expensive.
Choosing the right type depends on the procedure, dentist preference, and desired patient comfort.
10. Maintenance and Sterilisation
Proper care of dental handpieces is essential for performance, longevity, and patient safety:
- Cleaning: Remove debris and lubricate moving parts regularly.
- Sterilisation: Autoclaving or approved sterilisation methods prevent cross-contamination.
- Inspection: Check for wear, vibration, or noise that could indicate damage.
- Replacement: Worn burs or components should be replaced promptly to maintain efficiency and safety.
Consistent maintenance ensures handpieces operate smoothly and meet hygiene standards in the dental clinic.
11. Choosing the Right Handpiece for Your Practice
Selecting the right dental handpiece depends on the specific needs of your practice, the types of procedures you perform most frequently, and the comfort of both patients and staff. High-volume practices may benefit from durable, low-maintenance electric handpieces, while smaller clinics or mobile services might prioritise lightweight, air-driven models for portability and speed. It’s also important to consider ergonomics and noise levels to reduce operator fatigue and patient anxiety. Investing in versatile, high-quality handpieces ensures efficiency, precision, and safety across all treatments, ultimately improving outcomes and enhancing the overall patient experience.
Conclusion
Dental handpieces are integral to modern dental practice, enabling precision, efficiency, and patient comfort across a wide range of procedures. From high-speed and low-speed models to electric, air-driven, surgical, and fibre-optic handpieces, each type serves a specific purpose, offering unique advantages in performance, control, and safety.
Understanding the different types of dental handpieces, their applications, and maintenance requirements allows dental professionals to provide high-quality care while ensuring patient safety and comfort. Regular upkeep and careful selection of handpieces improve the efficiency of procedures and contribute to better treatment outcomes. For patients, having insight into these essential tools can reduce anxiety, increase trust, and foster confidence in the dental care they receive.

 Dental Infection Treatment and the Evolution of Advanced Dental Technology
Dental Infection Treatment and the Evolution of Advanced Dental Technology  Deep Cleaning Woodland Hills: Understanding Gum Health and Advanced Dental Cleaning
Deep Cleaning Woodland Hills: Understanding Gum Health and Advanced Dental Cleaning  Dental Implants and Osteoporosis: What Patients Should Know About Safety and Healing
Dental Implants and Osteoporosis: What Patients Should Know About Safety and Healing  Improving Your Smile in Woodland Hills: A Balanced Approach to Confidence and Oral Care
Improving Your Smile in Woodland Hills: A Balanced Approach to Confidence and Oral Care  The Step by Step Process of Getting Dental Implants in Fargo
The Step by Step Process of Getting Dental Implants in Fargo  Dr. Kami Hoss Discusses the Importance of Prioritizing Oral Health
Dr. Kami Hoss Discusses the Importance of Prioritizing Oral Health  How Anti Aging Clinics Personalize Treatment Plans for Different Skin Types
How Anti Aging Clinics Personalize Treatment Plans for Different Skin Types  Discover the Best TRT Clinic in Boston: Your Guide to Quality Hormone Care
Discover the Best TRT Clinic in Boston: Your Guide to Quality Hormone Care  Best Nicotine Gum Options: Key Benefits and How to Choose the Right One
Best Nicotine Gum Options: Key Benefits and How to Choose the Right One